 or
or  .
.
Dilation modules are reiterative: repeating an erosion or dilation of size 1 N times has the same effect as performing a single erosion with a structuring element of size N.
In figure 1, the binary image is I, and X denotes the set of points with a value of 1. The dilation of I by the structuring element B results in the set of points x,
where the disc representing B and centered on x has a non empty intersection with the set of points X. The dilation of I can be denoted as  or
or  .
.
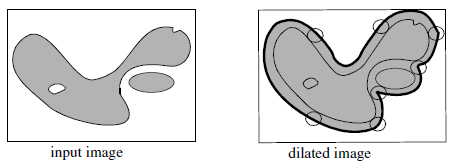
| Figure 1: Dilation applied to a binary image |
The dilated set of X by the structuring element B is:

It may also be expressed as:

The value of the structuring element (B) varies depending on the type of erosion. On a gray level image, the dilation by the structuring element B is the search for the maximum value of intensities within B:
2D image :  .
.
3D image :  .
.
When the point hits the edge of the image, the structuring element is composed of the intersection of B with the points of the structuring element totally within the image, and not the points outside the image.