Sequential Analysis of the Origin of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus
This example shows pairwise sequence alignment (PWSA). PWSA has multiple applications in bioinformatics, such as multiple sequence analysis and phylogenetic tree reconstruction. We look at a PWSA that uses a global dynamic programming algorithm to align each pair of sequences, and we then calculate the pairwise distances using the Tajima-Nei metric. This gives us a matrix of distances between sequences that we use for inferring the phylogeny of HIV and SIV viruses. PWSA is a computationally expensive task with complexity O(L*L*N*N), where L is the average length of the sequences and N is the number of sequences [Durbin, et al. Cambridge University Press, 1998].
For details about the computations, view the code for pctdemo_setup_hivview the code for pctdemo_setup_hiv.
Prerequisites:
Related examples:
Load the Example Settings and the Data
We start by getting the example difficulty level. If you want to use a different example difficulty level, use paralleldemoconfig and then run this example again. See Customizing the Settings for the Examples in the Parallel Computing Toolbox for full details.
difficulty = pctdemo_helper_getDefaults();
The pctdemo_setup_hiv function retrieves the protein sequence information from the NCBI GenBank® database, and the difficulty parameter controls how many protein sequences we retrieve. You can view the code for pctdemo_setup_hivview the code for pctdemo_setup_hiv for full details.
[fig, pol, description] = pctdemo_setup_hiv(difficulty); numViruses = length(pol); startTime = clock;
Downloading data from the NCBI GenBank database Finished downloading
Calculate the Distances
We call seqpdist to align the POL sequences and use the Tajima-Nei metric to measure the distances between them.
pold = seqpdist(pol, 'method', 'Tajima-Nei', 'Alphabet', 'NT', ... 'indel', 'pair');
Measure the Elapsed Time
The time used for the sequential computations should be compared against the time it takes to perform the same set of calculations using the Parallel Computing Toolbox in the Distributed Analysis of the Origin of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus example. The elapsed time varies with the underlying hardware.
elapsedTime = etime(clock, startTime);
fprintf('Elapsed time is %2.1f seconds\n', elapsedTime);
Elapsed time is 12.6 seconds
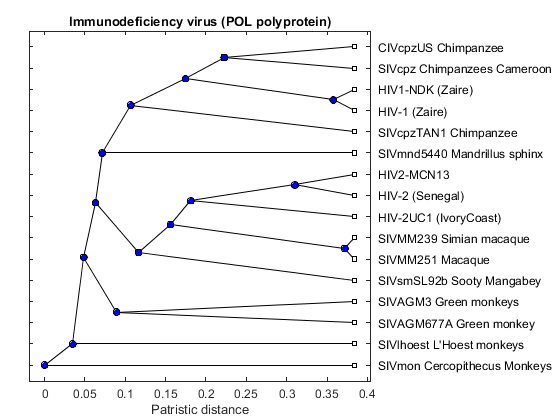
Plot the Results
Now that we have all the distances, we can construct the phylogenetic tree for the POL proteins. You can view the code for pctdemo_plot_hivview the code for pctdemo_plot_hiv for full details.
pctdemo_plot_hiv(fig, pold, description);