Optimization App with the fmincon Solver
This example shows how to use the Optimization app with the fmincon solver
to minimize a quadratic subject to linear and nonlinear constraints
and bounds.
Note: The Optimization app warns that it will be removed in a future release. |
Consider the problem of finding [x1, x2] that solves
subject to the constraints
The starting guess for this problem is x1 = 3 and x2 = 1.
Step 1: Write a file objecfun.m for the objective function.
function f = objecfun(x) f = x(1)^2 + x(2)^2;
Step 2: Write a file nonlconstr.m for the nonlinear constraints.
function [c,ceq] = nonlconstr(x)
c = [-x(1)^2 - x(2)^2 + 1;
-9*x(1)^2 - x(2)^2 + 9;
-x(1)^2 + x(2);
-x(2)^2 + x(1)];
ceq = [];Step 3: Set up and run the problem with the Optimization app.
Enter
optimtoolin the Command Window to open the Optimization app.Select
fminconfrom the selection of solvers and change the Algorithm field toActive set.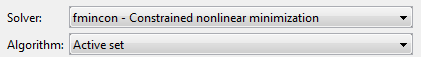
Enter
@objecfunin the Objective function field to call theobjecfun.mfile.Enter
[3;1]in the Start point field.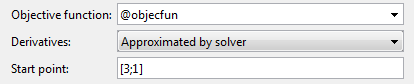
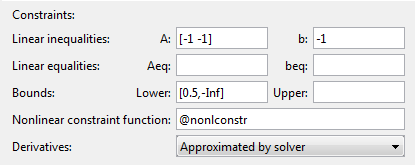
Define the constraints.
Set the bound
0.5≤ x1 by entering[0.5,-Inf]in the Lower field. The-Infentry means there is no lower bound on x2.Set the linear inequality constraint by entering
[-1 -1]in the A field and enter-1in the b field.Set the nonlinear constraints by entering
@nonlconstrin the Nonlinear constraint function field.
In the Options pane, expand the Display to command window option if necessary, and select
Iterativeto show algorithm information at the Command Window for each iteration.
Click the Start button as shown in the following figure.
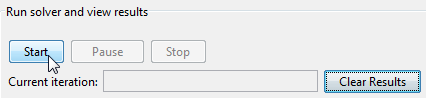
When the algorithm terminates, under Run solver and view results the following information is displayed:
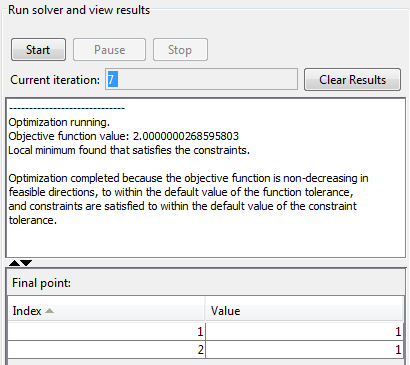
The Current iteration value when the algorithm terminated, which for this example is
7.The final value of the objective function when the algorithm terminated:
Objective function value: 2.0000000268595803
The algorithm termination message:
Local minimum found that satisfies the constraints. Optimization completed because the objective function is non-decreasing in feasible directions, to within the default value of the function tolerance, and constraints are satisfied to within the default value of the constraint tolerance.
The final point, which for this example is
1 1
In the Command Window, the algorithm information is displayed for each iteration:
Max Line search Directional First-order Iter F-count f(x) constraint steplength derivative optimality Procedure 0 3 10 2 Infeasible start point 1 6 4.84298 -0.1322 1 -5.22 1.74 2 9 4.0251 -0.01168 1 -4.39 4.08 Hessian modified twice 3 12 2.42704 -0.03214 1 -3.85 1.09 4 15 2.03615 -0.004728 1 -3.04 0.995 Hessian modified twice 5 18 2.00033 -5.596e-005 1 -2.82 0.0664 Hessian modified twice 6 21 2 -5.327e-009 1 -2.81 0.000522 Hessian modified twice Local minimum found that satisfies the constraints. Optimization completed because the objective function is non-decreasing in feasible directions, to within the default value of the function tolerance, and constraints are satisfied to within the default value of the constraint tolerance. Active inequalities (to within options.TolCon = 1e-006): lower upper ineqlin ineqnonlin 3 4