Create a Python Application with MATLAB Code
This example shows how to create a Python® package using a MATLAB® function. You can then pass the generated package to the developer, who is responsible for integrating it into an application.
To compile a Python package from MATLAB code:
In MATLAB, examine the MATLAB code that you want to deploy as a Python package. The example used here is
makesqr.m, located inmatlabroot\toolbox\javabuilder\Examples\MagicSquareExample\MagicDemoCompOpen
makesqr.m.function y = makesqr(x) y = magic(x);At the MATLAB command prompt, enter
makesqr(3).The output appears as follows:
ans = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2
Open the Library Compiler app.
On the toolstrip, select the Apps tab.
Click the arrow at the far right of the tab to open the apps gallery.
Click Library Compiler.
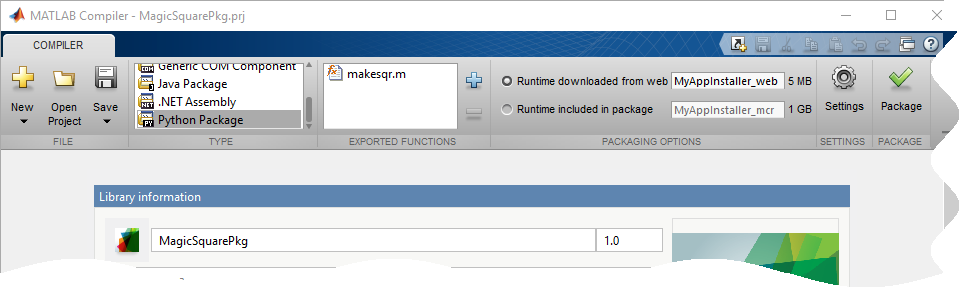
In the Application Type section of the toolstrip, select Python Package from the list.
Specify the MATLAB functions you want to deploy.
In the Exported Functions section of the toolstrip, click the plus button.
In the file explorer that opens, locate and select the
makesqr.mfile.makesqr.mis located inmatlabroot\toolbox\javabuilder\Examples\MagicSquareExample\MagicDemoCompClick Open to select the file, and close the file explorer.
makesqr.m is added to the list of exported files and a minus button appears under the plus button. In addition,
makesqris set as the package name.
In the top field of Application Information, replace Library Name
makesqrwithMagicSquarePkg.For more information on naming requirement for the Python package, see Import Compiled Python Packages.
In the Packaging Options section of the toolstrip, verify that the Runtime downloaded from web check box is selected.
This option creates an application installer that automatically downloads the MATLAB Runtime and installs it along with the deployed package.
Click Save to specify a project name and save the project.
Click Package.
Select the Open output folder when process completes check box.
Verify that the generated output contains:
for_redistribution— A folder containing the installer to distribute the packagefor_testing— A folder containing the raw generated files to create the installerfor_redistribution_files_only— A folder containing only the files needed to redistribute the packagePackagingLog.txt— A log file generated by the compiler
Click Close on the Package window.
Open a command prompt in the
for_redistribution_files_onlyfolder.Run the setup script to install the package.
python setup.py install
Create a new file called
getmagic.py. Paste the following code into the file.import MagicSquarePkg myMagic = MagicSquarePkg.initialize() print(myMagic.makesqr(3)) myMagic.terminate()
From the system's command prompt, run the application.
python getmagic.py
The following output will be displayed:
[[8.0,1.0,6.0], [3.0,5.0,7.0], [4.0,9.0,2.0]]
Note
On Mac OS X you must use the
mwpythonscript. Themwpythonscript is located in thematlabroot/binmatlabrootis the location of your MATLAB installation. For example:mwpython getmagic.py