Compile Python Packages with Library Compiler App
Note
MATLAB® Compiler SDK™ cannot compile MATLAB code that uses the MATLAB Python® interface.
To compile MATLAB code into a Python package:
Open the Library Compiler app.
On the toolstrip, select the Apps tab.
Click the arrow at the far right of the tab to open the apps gallery.
Click Library Compiler.
Note
You can also start the Library Compiler app using the
libraryCompilerfunction.
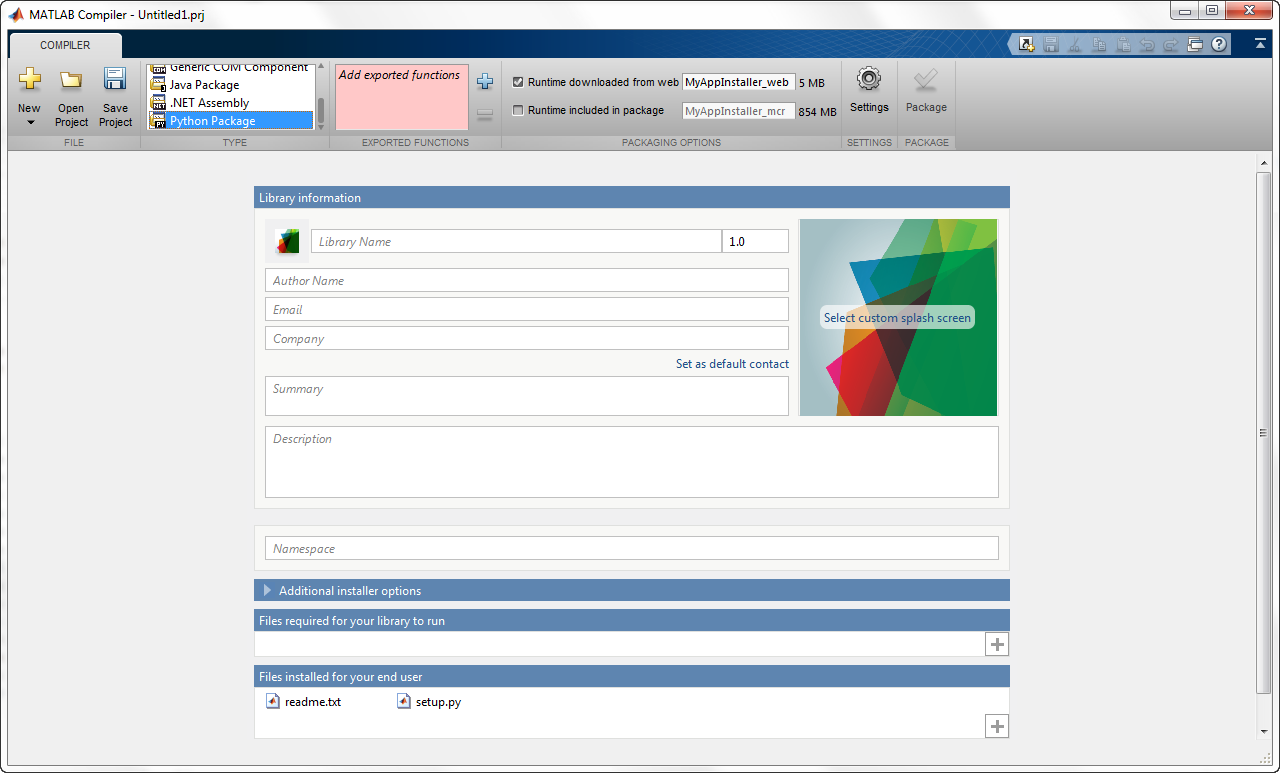
In the Application Type section of the toolstrip, select Python Package.
Note
If the Application Type section of the toolstrip is collapsed, expand it by clicking the down arrow.
Specify the MATLAB files you want deployed in the package.
In the Exported Functions section of the toolstrip, click the plus button.
Note
If the Exported Functions section of the toolstrip is collapsed, expand it by clicking the down arrow.
In the file explorer that opens, locate and select one or more MATLAB files.
Click Open to select the file and close the file explorer.
The names of the selected files are added to the list and a minus button appears below the plus button. The name of the first file listed is used as the default application name and the default package name.
Verify that the function defined in the selected files is properly mapped into a namespace.

In the Packaging Options section of the toolstrip, specify how the installer will deliver the MATLAB Runtime with the package.
Note
If the Packaging Options section of the toolstrip is collapsed, expand it by clicking the down arrow.
You can select one or both of the following options:
Runtime downloaded from web — Generates an installer that downloads the MATLAB Runtime installer from the web.
Runtime included in package — Generates an installer that includes the MATLAB Runtime installer.
Note
Selecting both options creates two installers.
Regardless of the options selected the generated installer scans the target system to determine if there is an existing installation of the appropriate MATLAB Runtime. If there is not, the installer installs the MATLAB Runtime.
Specify the name of any generated installers.
In the Application Information and Additional Installer Options sections of the app, customize the look and feel of the generated installer.
You can change the information used to identify the application data used by the installer:
Splash screen
Installer icon
Package version
Name and contact information of the package’s author
Brief summary of the package’s purpose
Detailed description of the package
You can also change the default location into which the package is installed and provide some notes to the installer.
All the provided information is displayed as the installer runs.
For more information, see Customize the Installer.
In the Files required for your application to run section of the app, verify that the files required by the deployed MATLAB functions are listed.
Note
These files are compiled into the generated binaries along with the exported files.
In general, the built-in dependency checker will automatically populate this section with the appropriate files. However, if needed you can manually add any files it missed.
For more information, see Manage Required Files in Compiler Project.
In the Files installed for your end user section of the app, verify that any additional non-MATLAB files you want installed with the application are listed.
Note
These files are placed in the
applicationsfolder of the installation.This section automatically lists:
Generated package
Python setup script
Readme file
You can manually add files to the list. Additional files can include documentation, sample data files, and examples to accompany the application.
For more information, see Specify Files to Install with Application.
Click the Settings button to customize the flags passed to the compiler and the folders to which the generated files are written.
Click the Package button to compile the MATLAB code and generate any installers.
Verify that the generated output contains:
for_redistribution— A folder containing the installer to distribute the packagefor_testing— A folder containing the raw generated files to create the installerfor_redistribution_files_only— A folder containing only the files needed to redistribute the packagePackagingLog.txt— A log file generated by the compiler