Create and Use Distributed Arrays
If your data is currently in the memory of your local machine,
you can use the distributed function to distribute
an existing array from the client workspace to the workers of a parallel
pool. Distributed arrays use the combined memory
of multiple workers in a parallel pool to store the elements of an
array. For alternative ways of partitioning data, see Distributing Arrays.You
can use distributed arrays to scale up your big
data computation. Consider distributed arrays
when you have access to a cluster, as you can combine the memory of
multiple machines in your cluster.
A distributed array is a single variable,
split over multiple workers in your parallel pool. You can work with
this variable as one single entity, without having to worry about
its distributed nature. Explore the functionalities available for distributed arrays
in the Parallel
Computing Toolbox™: Using MATLAB Functions on Distributed Arrays.
When you create a distributed array, you
cannot control the details of the distribution. On the other hand, codistributed arrays
allow you to control all aspects of distribution, including dimensions
and partitions. In the following, you learn how to create both distributed and codistributed arrays.
Creating Distributed Arrays
You can create a distributed array in different ways:
Use the
distributedfunction to distribute an existing array from the client workspace to the workers of a parallel pool.You can directly construct a distributed array on the workers. You do not need to first create the array in the client, so that client workspace memory requirements are reduced. The functions available include
eye(___,'distributed')rand(___,'distributed')distributedobject reference page.Create a
codistributedarray inside anspmdstatement, see Single Program Multiple Data (spmd). Then access it as adistributedarray outside thespmdstatement. This lets you use distribution schemes other than the default.
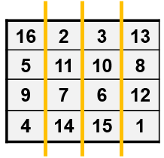
In this example, you create an array in the client workspace, then turn it into a distributed array:
parpool('local',4) % Create pool A = magic(4); % Create magic 4-by-4 matrix B = distributed(A); % Distribute to the workers B % View results in client. whos % B is a distributed array here. delete(gcp) % Stop pool
You have createdB as a distributed array,
split over the workers in your parallel pool. This is shown in the
figure.
Creating Codistributed Arrays
Unlike distributed arrays, codistributed arrays
allow you to control all aspects of distribution, including dimensions
and partitions. You can create a codistributed array
in different ways:
Partitioning a Larger Array — Start with a large array that is replicated on all workers, and partition it so that the pieces are distributed across the workers. This is most useful when you have sufficient memory to store the initial replicated array.
Building from Smaller Arrays — Start with smaller replicated arrays stored on each worker, and combine them so that each array becomes a segment of a larger codistributed array. This method reduces memory requirements as it lets you build a codistributed array from smaller pieces.
Using MATLAB Constructor Functions — Use any of the MATLAB® constructor functions like
randorzeroswith a codistributor object argument. These functions offer a quick means of constructing a codistributed array of any size in just one step.
In this example, you create a codistributed array
inside an spmd statement, using a nondefault distribution
scheme. First, define 1-D distribution along the third dimension,
with 4 parts on worker 1, and 12 parts on worker 2. Then create a
3-by-3-by-16 array of zeros.
parpool('local',2) % Create pool spmd codist = codistributor1d(3,[4,12]); Z = zeros(3,3,16,codist); Z = Z + labindex; end Z % View results in client. whos % Z is a distributed array here. delete(gcp) % Stop pool
For more details on codistributed arrays, see Working with Codistributed Arrays.