Module: Diametrical Variation ()
For an introduction, see section Analysis.
This module measure the number of entries in an object along a given direction. Let's consider a set of lines
, parallel to a direction
, and regularly spaced by
.
The diameter variation is defined as:
Where
is the number of boundary points which intersect the set of lines
. This is equivalent to the sum of the lengths of the projections of the object in the
direction.
Note that
is symmetric:
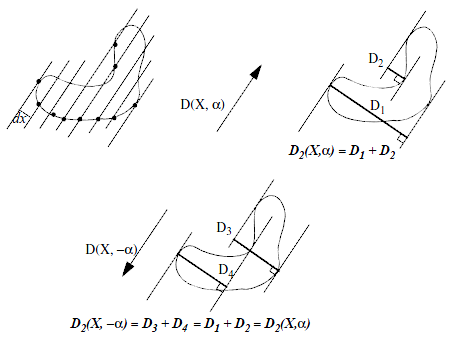
Figure 1: Application of the Diametrical Variation formula The discrete case in 2D translates to the search for specific configurations, as defined in the table below.
See also: Area, Euler Number, Fractal Dimension, Moments Of Inertia, Volume Fraction.
Input Binary Image [required]
The image to be processed. Supported type is: binary image (Uniform Label Field with 2 labels).
Interpretation
This port specifies whether the input will be interpreted as a 3D volume or a stack of 2D images for processing.
- "3D": the module configuration is set to 3D. The image will be processed as a whole in 3D.
- "XY planes": the module configuration is set to 2D. The image will be processed slice per slice.