Reserving Memory for Deployed Applications with MATLAB Memory Shielding
What Is MATLAB Memory Shielding and When Should You Use It?
Occasionally you encounter problems ensuring that you have the memory needed to run deployed applications. These problems often occur when:
Your data set is large
You are trying to compensate for the memory limitations inherent in a 32-bit Windows® system
The computer available to you has limited resources
Network resources are restrictive
Use MATLAB® Memory Shielding to ensure that you obtain the maximum amount of contiguous memory to run your deployed application successfully.
MATLAB Memory Shielding provides the specified level of protection of the address space used by MATLAB. When you use this feature, it reserves the largest contiguous block of memory available for your application after startup.
Memory shielding works by ensuring that resources, such as DLLs, load into locations that will not fragment the address space of the system. The feature provides the specified amount of contiguous address space you specify, up to the maximum available on the system.
For example, on a 32-bit Windows system, MATLAB defaults
to memory shielding for virtual addresses 0x50000000-0x70000000.
At the point where your application runs, the shield lowers, allowing
allocation of that virtual address space.
Note:
This topic describes how to invoke the shielding function for
deployed applications, not the MATLAB workspace. To learn more
about invoking memory shielding for MATLAB workspaces, see the
discussion of the start-up option |
Requirements for Using MATLAB Memory Shielding
Before using MATLAB Memory Shielding for your deployed applications, verify that you meet the following requirements:
Your deployed application is failing because it cannot find the proper amount of memory and not for another unrelated reason. As a best practice, let the operating system attempt to satisfy runtime memory requests, if possible. See What Is MATLAB Memory Shielding and When Should You Use It? for examples of cases where you can benefit by using MATLAB Memory Shielding
Your application runs on a Windows 32-bit system. While MATLAB Memory Shielding runs on 64-bit Windows systems without failing, it has no effect on your application.
You are running with a standalone application or Windows executable. MATLAB Memory Shielding does not work with shared libraries, .NET assemblies or Java® packages.
You have run the MATLAB Compiler Runtime Installer on your system to get the MATLAB Runtime. The memory shielding feature is installed with the MATLAB Runtime.
Invoking MATLAB Memory Shielding for Your Deployed Application
Invoke memory shielding by using either the command-line syntax or the GUI. Each approach has appropriate uses based on your specific memory reservation needs.
Using the Command Line
Use the command line if you want to invoke memory shielding
only with the various shield_level values
(not specific address ranges).
The base command-line syntax is:
MemShieldStarter [-help] [-gui]
[-shield shield_level]
fully-qualified_app_path
[user-defined_app_arguments]
Run your application using the default level of memory shielding. Use the command:
MemShieldStarter fully-qualified_app_path [user-defined_app_arguments]If your application runs successfully, try the next highest shield level to guarantee more contiguous memory, if needed.
A higher level of protection does not always provide a larger size block and can occasionally cause start-up problems. Therefore, start with a lower level of protection and be conservative when raising the level of protection.
Use only memory shielding levels that guarantee a successful execution of your application. See the table MemShieldStarter Options for more details on which shield options to choose.
Contact your system administrator for further advice on successfully running your application.
If your application fails to start, disable memory shielding:
To disable memory shielding after you have enabled it, run the following command:
MemShieldStarter -shield none fully-qualified_app_path [user-defined_app_arguments]
Contact your system administrator for further advice on successfully running your application.
MemShieldStarter Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Invokes help for |
| Starts the Windows graphical interface for |
| See Shield Level Options. |
| The fully qualified path to your user application |
| Arguments passed to your user application. |
Shield Level Options. shield_level options are as follows:
none— This value completely disables memory shielding. Use this value if your application fails to start successfully with the default (-shield minimum) option.minimum— The option defaults to this setting. Minimum shielding protects the range0x50000000to0x70000000during startup until just before processingmatlabrc. This value ensures at least approximately 500 MB of contiguous memory available up to this point.When experimenting with a shielding level. start with
minimum. To use the default, do not specify a shield option upon startup. If your application fails to start successfully usingminimum, use-shield none. If your application starts successfully with the default value forshield_level, try using the-shield mediumoption to guarantee more memory.medium— This value protects the same range asminimum,0x50000000to0x70000000, but protects the range until just after startup processesmatlabrc. It ensures that there is at least approximately 500 MB of contiguous memory up to this point. If MATLAB fails to start successfully with the-shield mediumoption, use the default option (-shield minimum). If MATLAB starts successfully with the-shield mediumoption and you want to try to ensure an even larger contiguous block after startup, try using the-shield maximumoption.maximum— This value protects the maximum range, which can be up to approximately 1.5 GB, until just after startup processesmatlabrc. The default memory shielding range formaximumcovers0x10000000to0x78000000. If MATLAB fails to start successfully with the-shield maximumoption, use the-shield mediumoption.Note: The shielding range may vary in various locales. Contact your system administrator for further details.
Using the GUI
Use the graphical interface to invoke memory shielding for specific
address ranges as well as with specific shield_level values.
To start the GUI, run the following at the system command prompt:
The Memory Shielding Starter dialog box opens:MemShieldStarter -gui
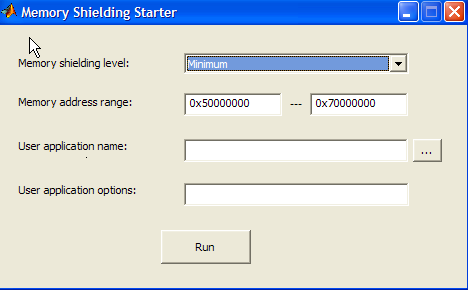
Enter the appropriate values as described in MemShieldStarter Options. Use the default Memory shielding level
minimum.You can specify a specific address range in the Memory address range fields. Specifying a range override the default
0x50000000through0x70000000address range values required for theshield_levelminimum, for example.Click Run.
If your application runs successfully, try the next highest shield level to guarantee more contiguous memory, if needed.
A higher level of protection does not always provide a larger size block and can occasionally cause startup problems. Therefore, start with a lower level of protection and use only what is necessary to guarantee a successful execution of your application.
See the table MemShieldStarter Options for more details on appropriate shield options for various situations.