Integrate an Add-In and COM Component with Microsoft Excel
Key Tasks for the Microsoft Excel End User
| Task | Reference |
|---|---|
| Verify that you have received all necessary files from the MATLAB® programmer. | Files Necessary for Deployment |
| Verify registry permissions for the add-in file and associated component. | Add-In and COM Component Registration |
| Execute your generated functions and create macros. | Execute Functions and Create Macros |
| Install the MATLAB Runtime on target systems and update system paths. | MATLAB Runtime |
| Use the Excel add-in. | Add-In Installation and Distribution |
Files Necessary for Deployment
Before beginning, verify that you have access to the following files:
The MCR Installer. For locations of all the MATLAB Runtime installers, run the
mcrinstallercommand..xlafile (the add-in).basfile (the generated VBA code).dllfilereadme.txt
Add-In and COM Component Registration
Note
COM components are used in both MATLAB Compiler™ and MATLAB Compiler SDK™, therefore some of the instructions relating to building and packaging COM components and add-ins can be shared between products.
When you create your COM component, it is registered in either HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE or HKEY_CURRENT_USER,
based on your log-in privileges.
If you find you need to change your run-time permissions due to security standards imposed by Microsoft® or your installation, you can do one of the following before deploying your COM component or add-in:
Log on as
administratorbefore running your COM component or add-inRun the following
mwregsvrcommand prior to running your COM component or add-in, as follows:where:mwregsvr [/u] [/s] [/useronly] project_name.dll
/uallows any user to unregister a COM component or add-in for this server/sruns this command silently, generating no messages. This is helpful for use in silent installations./useronlyallows only the currently logged-in user to run the COM component or add-in on this server
Caution
If your COM component is registered in the USER hive,
it will not be visible to Windows
Vista™ or Windows® 7 users
running as administrator on systems with UAC (User
Access Control) enabled.
If you register a component to the USER hive
under Windows 7 or Windows
Vista, your COM component may fail
to load when running with elevated (administrator)
privileges.
If this occurs, do the following to re-register the component
to the LOCAL MACHINE hive:
Unregister the component with this command:
mwregsvr /u /useronly my_dll.dll
Reregister the component to the
LOCAL MACHINEhive with this command:mwregsvr my_dll.dll
COM Component Incorporation into Microsoft Excel using the Function Wizard
Now that your add-in and COM component have been created, use the Function Wizard to integrate the COM component into Microsoft Excel®.
See Execute Functions and Create Macros for a complete example of how to execute functions and create macros using the Magic Square example in this chapter.
MATLAB Runtime
The MATLAB Runtime is an execution engine made up of the same shared libraries MATLAB uses to enable execution of MATLAB files on systems without an installed version of MATLAB.
The MATLAB Runtime is available for downloading from the web to simplify the distribution of your applications created using the MATLAB Compiler or the MATLAB Compiler SDK. Download the MATLAB Runtime from the MATLAB Runtime product page.
The MATLAB Runtime installer does the following:
Install the MATLAB Runtime.
Install the component assembly in the folder from which the installer is run.
Copy the
MWArrayassembly to the Global Assembly Cache (GAC), as part of installing the MATLAB Runtime.
MATLAB Runtime Prerequisites
The MATLAB Runtime installer requires administrator privileges to run.
The version of the MATLAB Runtime that runs your application on the target computer must be compatible with the version of MATLAB Compiler or MATLAB Compiler SDK that built the deployed code.
Do not install the MATLAB Runtime in MATLAB installation directories.
The MATLAB Runtime installer requires approximately 2 GB of disk space.
Add the MATLAB Runtime Installer to the Installer
This example shows how to include the MATLAB Runtime in the generated installer, using one of the compiler apps. The generated installer contains all files needed to run the standalone application or shared library built with MATLAB Compiler or MATLAB Compiler SDK and properly lays them out on a target system.
On the Packaging Options section of the compiler interface, select one or both of the following options:
Runtime downloaded from web — This option builds an installer that invokes the MATLAB Runtime installer from the MathWorks website.
Runtime included in package — The option includes the MATLAB Runtime installer into the generated installer.
Click Package.
Distribute the installer as needed.
Install the MATLAB Runtime
This example shows how to install the MATLAB Runtime on a system.
If you are given an installer containing the compiled artifacts, then the MATLAB Runtime is installed along with the application or shared library. If you are given just the raw binary files, download the MATLAB Runtime installer from the web and run the installer.
Note
If you are running on a platform other than Windows, modify the path on the target machine. Setting the paths enables your application to find the MATLAB Runtime. For more information on setting the path, see MATLAB Runtime Path Settings for Run-Time Deployment (MATLAB Compiler SDK).
Windows paths are set automatically. On Linux® and Mac, you can use the run script to set paths. See Using MATLAB Compiler on Mac or Linux for detailed information on performing all deployment tasks specifically with UNIX® variants such as Linux and Mac.
Where to find the MWArray API
The MATLAB Runtime also includes MWArray.dll,
which contains an API for exchanging data between your applications
and the MATLAB Runtime. You can find documentation for this API
in the Help folder of the installation.
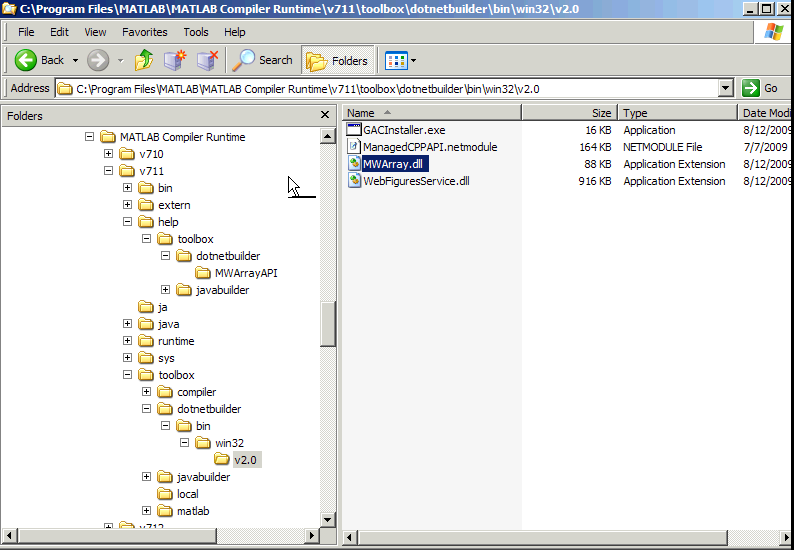
On target machines where the MATLAB Runtime installer is
run, it puts the MWArray assembly in mcrRoot\toolbox\dotnetbuilder\bin\architecture\framework_version
Sample Directory Structure of the MATLAB Runtime Including MWArray.dll
Add-In Installation and Distribution
Since Microsoft
Excel add-ins are written directly to the distrib folder
by MATLAB
Compiler, you and your end users install them exactly as you installed the
Function Wizard in Installation of the Function Wizard.
Calling Add-In Code from the Excel Spreadsheet
To run the executable code from a cell in the Excel spreadsheet,
invoke the add-in name with a method call. For example, if you deployed
a piece of MATLAB code called mymagic.m, or a figure
called mymagic.fig, you invoke that code by entering
the following in a cell in the spreadsheet:
=mymagic()
Tip
If the method call does not evaluate immediately, press Ctrl, Shift, and Enter simultaneously.