Introduction to Parallel Solutions
Run a Batch Job
To offload work from your MATLAB® session to run in the
background in another session, you can use the batch command. This example uses the for-loop
from the previous example, inside a script.
To create the script, type:
edit mywaveIn the MATLAB Editor, enter the text of the
for-loop:for i = 1:1024 A(i) = sin(i*2*pi/1024); end
Save the file and close the Editor.
Use the
batchcommand in the MATLAB Command Window to run your script on a separate MATLAB worker:job = batch('mywave')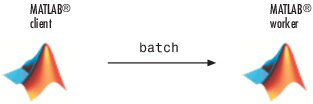
The
batchcommand does not block MATLAB, so you must wait for the job to finish before you can retrieve and view its results:wait(job)
The
loadcommand transfers variables created on the worker to the client workspace, where you can view the results:load(job,'A') plot(A)When the job is complete, permanently delete its data and remove its reference from the workspace:
delete(job) clear job
batch runs your code on a local worker
or a cluster worker, but does not require a parallel pool.
You can use batch to run either scripts
or functions. For more details, see the batch reference
page.
Run a Batch Parallel Loop
You can combine the abilities to offload a job and run a parallel
loop. In the previous two examples, you modified a for-loop
to make a parfor-loop, and you submitted a script
with a for-loop as a batch job. This example combines
the two to create a batch parfor-loop.
Open your script in the MATLAB Editor:
edit mywaveModify the script so that the
forstatement is aparforstatement:parfor i = 1:1024 A(i) = sin(i*2*pi/1024); end
Save the file and close the Editor.
Run the script in MATLAB with the
batchcommand as before, but indicate that the script should use a parallel pool for the loop:job = batch('mywave','Pool',3)
This command specifies that three workers (in addition to the one running the batch script) are to evaluate the loop iterations. Therefore, this example uses a total of four local workers, including the one worker running the batch script. Altogether, there are five MATLAB sessions involved, as shown in the following diagram.
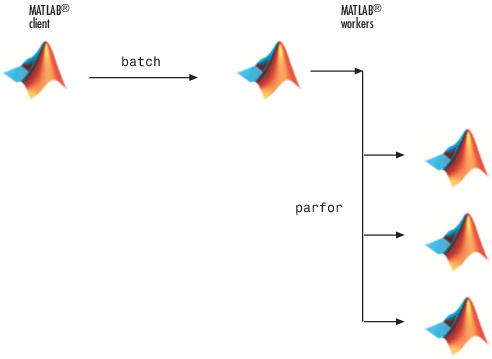
To view the results:
wait(job) load(job,'A') plot(A)The results look the same as before, however, there are two important differences in execution:
The work of defining the
parfor-loop and accumulating its results are offloaded to another MATLAB session bybatch.The loop iterations are distributed from one MATLAB worker to another set of workers running simultaneously (
'Pool'andparfor), so the loop might run faster than having only one worker execute it.
When the job is complete, permanently delete its data and remove its reference from the workspace:
delete(job) clear job
Run Script as Batch Job from the Current Folder Browser
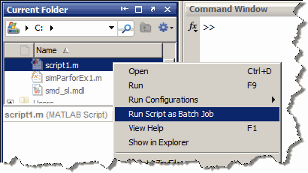
From the Current Folder browser, you can run a MATLAB script
as a batch job by browsing to the file’s folder, right-clicking
the file, and selecting Run Script as Batch Job.
The batch job runs on the cluster identified by the default cluster
profile. The following figure shows the menu option to run the script
file script1.m:
Running a script as a batch from the browser uses only one worker
from the cluster. So even if the script contains a parfor loop
or spmd block, it does not open an additional
pool of workers on the cluster. These code blocks execute on the single
worker used for the batch job. If your batch script requires opening
an additional pool of workers, you can run it from the command line,
as described in Run a Batch Parallel Loop.
When you run a batch job from the browser, this also opens the Job Monitor. The Job Monitor is a tool that lets you track your job in the scheduler queue. For more information about the Job Monitor and its capabilities, see Job Monitor.