Autoradiographs, corresponding histological section sets and radioactive [14C] standards are digitized with a flatbed scanner in transmission mode as either 8-bit or 16-bit grey-scale images (according to your scanner model).
In-plane digitization resolution needs to be sufficiently high to reveal the main structures of interest in the brain. Usually we choose a 600 dpi resolution (pixel size 42x42 mm2), for rat brain and a 1200 dpi resolution (pixel size 21x21 mm2), for the mouse one. The calibration scale available with the scanner gives the relation between optical density and gray level values in the autoradiographic images. As gray level calibration is critical for quantitative autoradiography analysis, make sure to use appropriate software for acquiring your images.A prerequisite for using BrainRAT process 02. image - individualizing and stacking multiple slices is that brain sections have been rigorously mounted on glass slides.
All the slice arrangements on glass slides are conceivable (Figure 3.4 and Figure 3.3). Yet, the following condition shall be respected as far as possible: ONLY ONE arrangement for the whole dataset The slice arrangements chosen by operator during the sectioning process will be requested as parameter values when using process 02. image - individualizing and stacking multiple slices.Figure 3.3. All possible section arrangements on glass slides according to column first, which are managed by BrainRAT process 02. image - individualizing and stacking multiple slices.
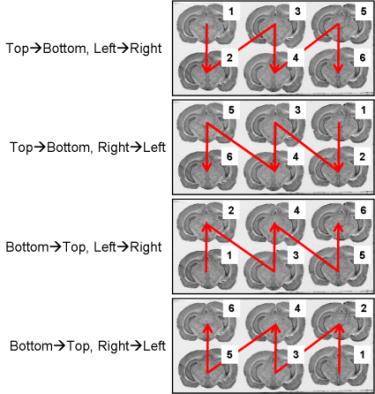 .
.
Figure 3.4. All possible section arrangements on glass slides according to line first, which are managed by BrainRAT process 02. image - individualizing and stacking multiple slices.
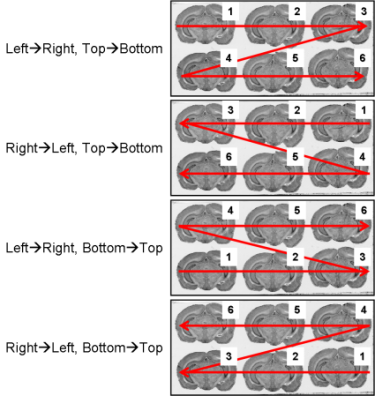 .
.
- Though an automated analysis of width and height parameters for each section according to median values have been implemented to detect and to correct for vertical and horizontal overlaps between two sections, try to let enough space between each line and each column to limit such a phenomenom (Figure 3.5).
- High-quality sections are essential to make the corresponding volumes spatially consistent in 3D. Indeed, the block-matching registration technique is based on both the section edges and the whole image, so the result of the 3D reconstruction will strongly depend on the information available in the sections to be processed, that is to say, on the quality of data.
Another prerequisite for using BrainRAT process 02. image - individualizing and stacking multiple slices is that the autoradiographic and histological sections have been acquired and stored under the form of glass slide column images called "overall scans" and whose size has been given by the scanner's field of view.
After the sectioning process, brain sections were exposed for several days to an autoradiographic film by arranging glass slides one below the other. Hence, the acquisition of autoradiographic sections can be achieved by digitizing the autoradiographic film, previously laid down on the surface of the scanner (Figure 3.6 (a)). The acquisition of homologous histological sections (same sections as those processed for autoradiography or adjacent sections coming from another batch) can then be achieved by directly laying down glass slides, arranged one below the other, on the surface of the scanner (Figure 3.6 (b)).Figure 3.6. (a) Acquisition of autoradiographic sections and corresponding radioactive [14C] standards. (b) Acquisition of homologous histological stained sections.
(a)![(a) Acquisition of autoradiographic sections and corresponding radioactive [14C] standards. (b) Acquisition of homologous histological stained sections.](./images/scanauto.png) (b)
(b)![(a) Acquisition of autoradiographic sections and corresponding radioactive [14C] standards. (b) Acquisition of homologous histological stained sections.](./images/scancresyl.png) .
.
Figure 3.7. Arrangement of glass slides on the surface of the scanner: Top->Bottom and Bottom->Top.
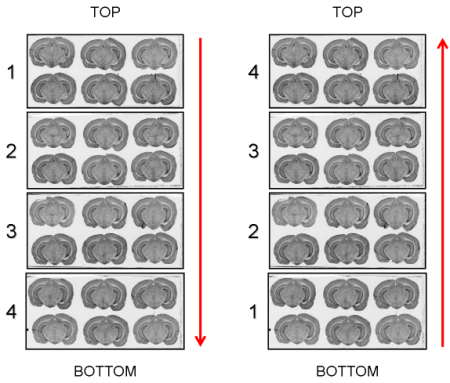 .
.
-
An a priori knowledge of section number and surface is used to perform iterative erosions, and thereby identify and extract the main connected components in the binary image of an overall scan. Consequently:
- There must not have objects with a similar surface in the image (e.g. handwritten section number);
- If important variations in section surface are observed from one glass slide to another, do not acquire too much glass slides together as a same overall scan;
- Changes in the original geometry of each section due to the mounting on glass slides may appear and induce the separation of some parts of the brain (olfactory bulb, occipital cortex, etc.). If necessary, a pre-processing can be required to artificially put back together these parts, using image manipulation software.
- If several batches have been obtained from adjacent sections (several stain dyes, immunohistochemistry, etc.), make sure that the sections acquired together come from the same batch.

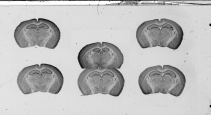
![(a) Overall scan of histological sections stained with cresyl violet (three glass slides arranged in a column, 600 dpi). (b) Overall scan of corresponding [14C]-2DG autoradiographic sections. (c) Radioactive [14C] standards.](./images/col_cresyl.png)
![(a) Overall scan of histological sections stained with cresyl violet (three glass slides arranged in a column, 600 dpi). (b) Overall scan of corresponding [14C]-2DG autoradiographic sections. (c) Radioactive [14C] standards.](./images/col_auto.png)
![(a) Overall scan of histological sections stained with cresyl violet (three glass slides arranged in a column, 600 dpi). (b) Overall scan of corresponding [14C]-2DG autoradiographic sections. (c) Radioactive [14C] standards.](./images/standards.png)