Output Functions
What Is an Output Function?
For some problems, you might want output from an optimization algorithm at each iteration. For example, you might want to find the sequence of points that the algorithm computes and plot those points. To do this, create an output function that the optimization function calls at each iteration. See Output Function for details and syntax.
Generally, the solvers that can employ an output function are the ones that can take nonlinear functions as inputs. You can determine which solvers can have an output function by looking in the Options section of function reference pages, or by checking whether the Output function option is available in the Optimization app for a solver.
Example: Using Output Functions
What the Example Contains
The following example continues the one in Nonlinear Inequality Constraints, which calls the
function fmincon at the command line to solve a
nonlinear, constrained optimization problem. The example in this section
uses a function file to call fmincon. The file
also contains all the functions needed for the example, including:
The objective function
The constraint function
An output function that records the history of points computed by the algorithm for
fmincon. At each iteration of the algorithm forfmincon, the output function:Plots the current point computed by the algorithm.
Stores the point and its corresponding objective function value in a variable called
history, and stores the current search direction in a variable calledsearchdir. The search direction is a vector that points in the direction from the current point to the next one.
The code for the file is here: Writing the Example Function File.
Writing the Output Function
You specify the output function in options,
such as
options = optimoptions(@fmincon,'OutputFcn',@outfun)
where outfun is the name of the output function.
When you call an optimization function with options as
an input, the optimization function calls outfun at
each iteration of its algorithm.
In general, outfun can be any MATLAB® function,
but in this example, it is a nested function of the function file
described in Writing the Example Function File.
The following code defines the output function:
function stop = outfun(x,optimValues,state)
stop = false;
switch state
case 'init'
hold on
case 'iter'
% Concatenate current point and objective function
% value with history. x must be a row vector.
history.fval = [history.fval; optimValues.fval];
history.x = [history.x; x];
% Concatenate current search direction with
% searchdir.
searchdir = [searchdir;...
optimValues.searchdirection'];
plot(x(1),x(2),'o');
% Label points with iteration number.
% Add .15 to x(1) to separate label from plotted 'o'
text(x(1)+.15,x(2),num2str(optimValues.iteration));
case 'done'
hold off
otherwise
end
endSee Using Handles to Store Function Parameters in the MATLAB Programming Fundamentals documentation for more information about nested functions.
The arguments that the optimization function passes to outfun are:
x— The point computed by the algorithm at the current iterationoptimValues— Structure containing data from the current iterationThe example uses the following fields of
optimValues:optimValues.iteration— Number of the current iterationoptimValues.fval— Current objective function valueoptimValues.searchdirection— Current search direction
state— The current state of the algorithm ('init','interrupt','iter', or'done')
For more information about these arguments, see Output Function.
Writing the Example Function File
To create the function file for this example:
Open a new file in the MATLAB Editor.
Copy and paste the following code into the file:
function [history,searchdir] = runfmincon % Set up shared variables with OUTFUN history.x = []; history.fval = []; searchdir = []; % call optimization x0 = [-1 1]; options = optimoptions(@fmincon,'OutputFcn',@outfun,... 'Display','iter','Algorithm','active-set'); xsol = fmincon(@objfun,x0,[],[],[],[],[],[],@confun,options); function stop = outfun(x,optimValues,state) stop = false; switch state case 'init' hold on case 'iter' % Concatenate current point and objective function % value with history. x must be a row vector. history.fval = [history.fval; optimValues.fval]; history.x = [history.x; x]; % Concatenate current search direction with % searchdir. searchdir = [searchdir;... optimValues.searchdirection']; plot(x(1),x(2),'o'); % Label points with iteration number and add title. % Add .15 to x(1) to separate label from plotted 'o' text(x(1)+.15,x(2),... num2str(optimValues.iteration)); title('Sequence of Points Computed by fmincon'); case 'done' hold off otherwise end end function f = objfun(x) f = exp(x(1))*(4*x(1)^2 + 2*x(2)^2 + 4*x(1)*x(2) +... 2*x(2) + 1); end function [c, ceq] = confun(x) % Nonlinear inequality constraints c = [1.5 + x(1)*x(2) - x(1) - x(2); -x(1)*x(2) - 10]; % Nonlinear equality constraints ceq = []; end endSave the file as
runfmincon.min a folder on the MATLAB path.
Running the Example
To run the example, enter:
[history searchdir] = runfmincon;
This displays the following iterative output in the Command Window.
Max Line search Directional First-order
Iter F-count f(x) constraint steplength derivative optimality Procedure
0 3 1.8394 0.5 Infeasible
1 6 1.85127 -0.09197 1 0.109 0.778 start point
2 9 0.300167 9.33 1 -0.117 0.313 Hessian modified
3 12 0.529835 0.9209 1 0.12 0.232 twice
4 16 0.186965 -1.517 0.5 -0.224 0.13
5 19 0.0729085 0.3313 1 -0.121 0.054
6 22 0.0353323 -0.03303 1 -0.0542 0.0271
7 25 0.0235566 0.003184 1 -0.0271 0.00587
8 28 0.0235504 9.032e-008 1 -0.0146 8.51e-007
Local minimum found that satisfies the constraints.
Optimization completed because the objective function is non-decreasing in
feasible directions, to within the default value of the function tolerance,
and constraints are satisfied to within the default value of the constraint tolerance.
Active inequalities (to within options.TolCon = 1e-006):
lower upper ineqlin ineqnonlin
1
2The output history is a structure that contains
two fields:
history =
x: [9x2 double]
fval: [9x1 double]The fval field contains the objective function
values corresponding to the sequence of points computed by fmincon:
history.fval
ans =
1.8394
1.8513
0.3002
0.5298
0.1870
0.0729
0.0353
0.0236
0.0236These are the same values displayed in the iterative output
in the column with header f(x).
The x field of history contains
the sequence of points computed by the algorithm:
history.x ans = -1.0000 1.0000 -1.3679 1.2500 -5.5708 3.4699 -4.8000 2.2752 -6.7054 1.2618 -8.0679 1.0186 -9.0230 1.0532 -9.5471 1.0471 -9.5474 1.0474
This example displays a plot of this sequence of points, in which each point is labeled by its iteration number.
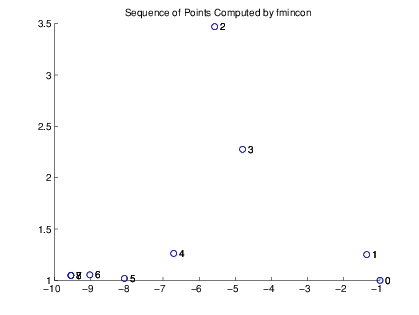
The optimal point occurs at the eighth iteration. Note that the last two points in the sequence are so close that they overlap.
The second output argument, searchdir, contains
the search directions for fmincon at each iteration.
The search direction is a vector pointing from the point computed
at the current iteration to the point computed at the next iteration:
searchdir =
-0.3679 0.2500
-4.2029 2.2199
0.7708 -1.1947
-3.8108 -2.0268
-1.3625 -0.2432
-0.9552 0.0346
-0.5241 -0.0061
-0.0003 0.0003